What Best Describes a Sunk Cost
The resources each of those scenarios focuses on is shown in the exhibit Testing Sunk Costs. A sunk cost is any cost that was expended in the past but can be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
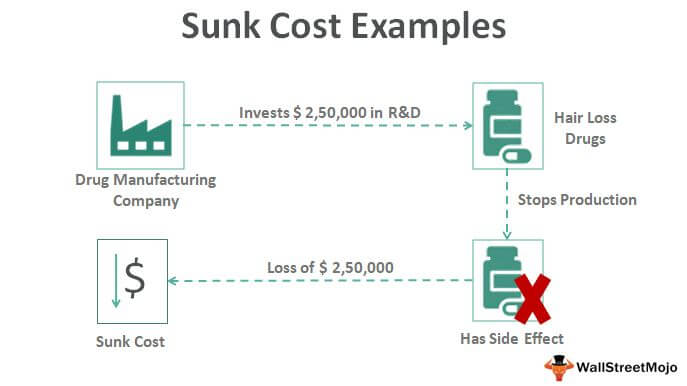
Sunk Cost Examples Top 4 Examples With Explanation
The definition of sunk costs Sunk costs in relation to stolen money When sunk costs should be considered in the decision making process The part played by.

. Any future costs associated with future decisions of the firm. Which of the following best describes an opportunity cost. The sunk cost fallacy is a logical fallacy or flawed argument for decision-making.
These costs are often irrelevant while considering a new investment or any new project. Sunk costs comes in the accounting cost since the company already pay for them. Costs which are incurred in the past.
Expected future data that differ among alternatives B. The cost of an asset that the company is considering replacing. The costs of electricity and utilities the firm uses each month.
Purchase price of vehicle to be traded in. A sunk cost is a cost that a company has already incurred and cant be recovered. Costs which are incurred in the past.
Sunk costs are cost that are sunk and cannot be recovered. A a cost which is irrelevant for the future B a cost which must be matched against the revenue C a cost which remains the same at all levels of production D a cost which varies with the level of production. Relevant costs are those costs that affects the decisionThese costs are considered analyzed while taking decisionThese are future costs that are yet to be incurred.
Since company has actually spent money on buying a machine cost of machine is already in the accounts. Cost incurred by the Firm as a result of the fire that broke into one of the Firms Godown. Which of the following statement best describes Sunk Costs.
Cost incurred by the Firm as result of bankruptcy of one of its Creditors. It is not a relevant cost in decision making but is part of the traditional accounting records. Which statement best describes a sunk cost.
The government then asked you it is illegal to build a house which is at such proximity to the main View the full answer. Which of the following best describes sunk costs. Sunk costs were formerly hard to deal with but once the NPV method came into wide use it became possible to simply include sunk costs in the cash flows and then calculate the PV.
Related Discussions- Sunk costs. Which of the following statement best describes Sunk Costs. A sunk cost is a cost that was incurred and expensed in the past and cannot be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
A factor that restricts the production or sale of a product. Benefits forgone by choosing a particular alternative course of action. Which of the following best describes a sunk cost.
The costs associated with a massive ad campaign the firm ran last month. Costs that were incurred in the past and cannot be changed. Which of the following statements best describes sunk costs.
Any future costs associated with future decisions of the firm. Costs that were incurred in the past and cannot be changed C. Fixed costs that may be avoided in the future are referred to as.
Setting off losses that the Firm incurred in the previous years. A sunk cost is any cost not directly related to the physical work required to complete the project. An opportunity cost is best described by which of the following.
Our analysis identified which scenarios gave responses that best described the most variation in the data. Learn more about the definition of sunk costs and explore examples of sunk costs in businesses. The costs associated with a massive ad campaign the firm ran last month.
Benefits foregone by choosing a particular alternative course of action D. The costs of electricity and utilities the firm uses each month. Sunk costs are irrelevant costThese costs have already been incurredThey do not affect future decisions.
Which of the following is a sunk cost. B A sunk cost is any cost that was expended in the past but can be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project. Which of the following best describes a sunk cost.
Costs of ingredients that firm uses to make food it sells to customers. For example - Lets say you were building a house which was proximate to the main road. 2 it is a relevant cost in decision making but is not part of the traditional accounting records.
A A sunk cost is any cost that must be expended in order to complete a project and bring it into operation. When we fall prey to the sunk cost fallacy we make irrational decisions that are against our best interestessentially digging ourselves into a deeper and deeper hole. Sunk costs refer to incurred costs that can no longer be recovered.
Irrelevant to the decision. Fixed costs that do not differ between two alternatives are. The term is usually used to describe persisting in a bad investment on the grounds that otherwise the time money or effort invested in the project will be wasted.
Cost incurred by the Firm as a result of the fire that broke into one of the Firms Godown. Cost incurred by the Firm as result of bankruptcy of one of its Creditors. Costs of ingredients that firm uses to make food it sells to customers.
Which of the following best describes sunk costs. In the sunk cost fallacy prior investment is cited as a reason for pursuing a course of action. The sunk cost fallacy is our tendency to continue with something weve invested money effort or time intoeven if the current costs outweigh the benefits.

The Sunk Cost Fallacy And Music Concerts By Sejal Gupta Medium
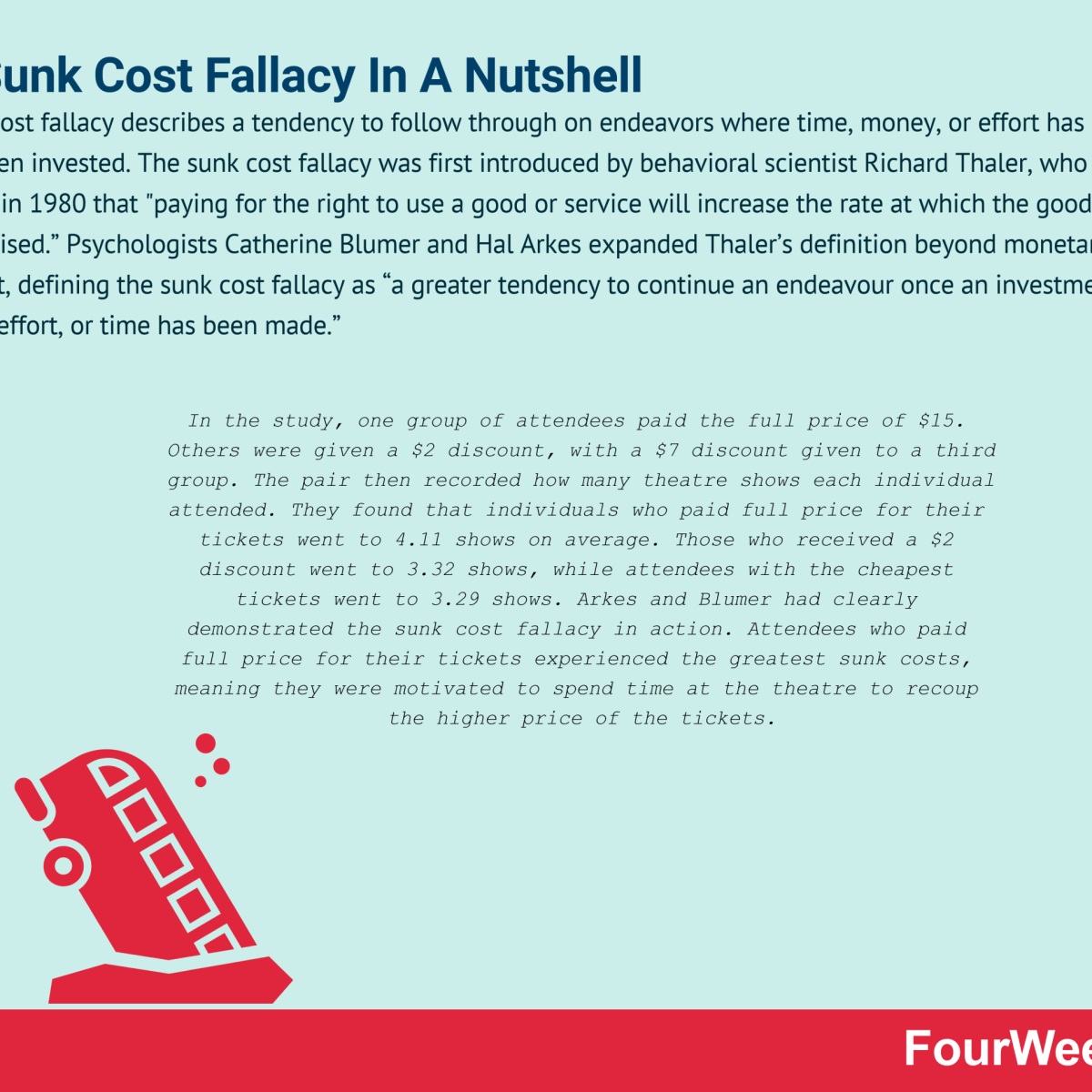
What Is The Sunk Cost Fallacy The Sunk Cost Fallacy In A Nutshell Fourweekmba

No comments for "What Best Describes a Sunk Cost"
Post a Comment